Nutrition Facts in Heavy Whipping Cream
Macronutrient Composition of Heavy Whipping Cream: Nutrition Facts In Heavy Whipping Cream

Nutrition facts in heavy whipping cream – Heavy whipping cream is a dairy product known for its high fat content and rich texture, making it a popular ingredient in various culinary applications. Understanding its macronutrient profile is crucial for those monitoring their dietary intake. This section details the macronutrient breakdown of heavy whipping cream, comparing it to other dairy products.
Macronutrient Breakdown of Heavy Whipping Cream
Heavy whipping cream’s primary characteristic is its high fat content. The following table provides a typical macronutrient breakdown per serving (approximately 1/2 cup or 118ml), although values can vary slightly depending on the brand and production methods. It’s important to always check the nutrition label on the specific product you are using.
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving | Percentage of Daily Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | 82g | 100%+ | grams |
| Protein | 2g | 4% | grams |
| Carbohydrates | 1g | 1% | grams |
Types of Fat in Heavy Whipping Cream and Their Health Implications
The fat in heavy whipping cream is primarily composed of saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats, while necessary in moderation, should be consumed in limited quantities as excessive intake is associated with increased cholesterol levels and an elevated risk of heart disease. Unsaturated fats, on the other hand, are considered healthier fats and contribute to overall cardiovascular health when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
The specific ratio of saturated to unsaturated fats can vary depending on the source of the cream and the animal’s diet. It’s crucial to remember that heavy whipping cream should be consumed sparingly as part of a balanced diet to minimize the potential negative health implications associated with its high saturated fat content.
Comparison to Other Dairy Products
Compared to other dairy products, heavy whipping cream stands out due to its significantly higher fat content. Whole milk, for instance, typically contains around 3.25% fat, while half-and-half falls somewhere in between, with approximately 10-18% fat. This difference in fat content directly impacts the calorie density of each product. Heavy whipping cream is considerably higher in calories due to its substantially greater fat content.
Choosing between these dairy products depends on individual dietary needs and preferences, considering factors such as calorie intake and fat consumption goals.
Alternatives to Heavy Whipping Cream

Heavy whipping cream, while delicious, is high in fat and calories. For those seeking healthier alternatives or needing a substitute for specific dietary needs or recipes, several options exist, each with its own unique characteristics and culinary applications. These alternatives offer a range of fat and calorie contents, influencing both their taste and how they perform in different dishes.
Comparison of Heavy Whipping Cream Alternatives
The following table details several alternatives to heavy whipping cream, highlighting their fat and calorie content, and comparing their taste and texture to the original. Choosing the right substitute depends heavily on the intended use and desired outcome.
| Alternative | Fat Content (approx. per 100g) | Calorie Content (approx. per 100g) | Taste/Texture Comparison to Heavy Whipping Cream |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coconut Cream (full-fat) | 55-60g | 550-600 kcal | Rich, slightly sweet, and coconutty flavor. Thicker consistency than heavy cream, whipping to a slightly less stiff peak. Can impart a noticeable coconut taste in some dishes. |
| Almond Cream | 20-30g | 250-350 kcal | Nutty flavor, less rich than heavy cream. Whipping properties vary depending on brand and additives; some may not whip as stiffly. Can be slightly thinner than heavy cream. |
| Low-Fat Whipping Cream | 10-20g | 150-250 kcal | Lighter taste and texture compared to heavy cream. Whipped consistency is less stable and may not hold its shape as well. Best suited for applications where a less rich and stable whipped topping is acceptable. |
| Cashew Cream (homemade) | Variable, depends on soaking and blending | Variable, depends on soaking and blending | Mild, slightly sweet, and creamy. Texture can be adjusted through blending and addition of liquids. Whipping properties are less predictable than heavy cream but can be used in some recipes. |
Culinary Applications of Heavy Whipping Cream Alternatives
The suitability of each alternative depends significantly on the recipe. For instance, full-fat coconut cream excels in recipes where its coconut flavor complements the other ingredients, such as curries or tropical desserts. However, its strong flavor might be overpowering in dishes requiring a neutral cream base. Low-fat whipping cream, due to its lighter texture and less stable whipped consistency, is better suited for sauces or less demanding whipped toppings where a less firm texture is acceptable.
Understanding nutrition facts is key to mindful eating. Heavy whipping cream, for example, is high in fat and calories, a fact often overlooked. However, comparing this to other beverages reveals interesting contrasts; check out the sugar content in mountain dew kickstart nutrition facts for a stark comparison. Returning to heavy whipping cream, remember moderation is crucial even with seemingly “natural” ingredients.
Almond cream, with its subtle nutty flavor, offers a versatile option for many applications but might not provide the same richness and volume as heavy whipping cream when whipped. Homemade cashew cream provides a creamy, neutral base, useful for sauces, soups, or dips. The choice of the best alternative often involves a trade-off between taste, texture, and health considerations.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information
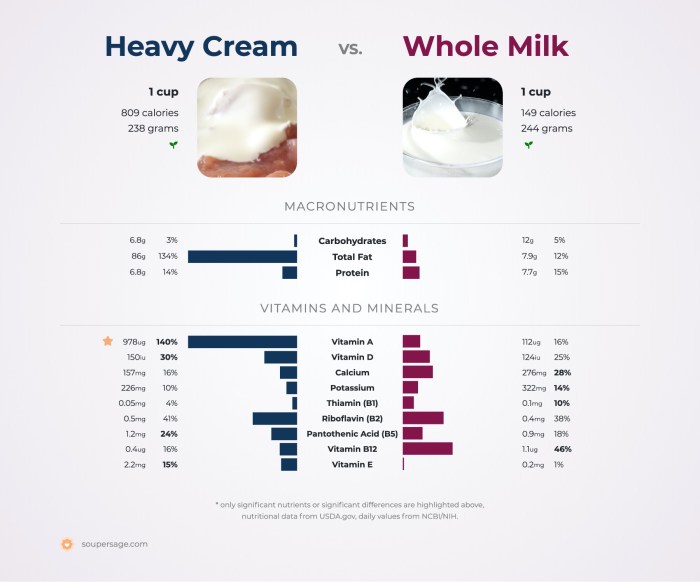
Heavy whipping cream’s nutritional profile, while rich in fat, can be effectively communicated to consumers through a clear and visually appealing infographic. A well-designed visual aids understanding and allows for quick comparison with other dairy products or alternative options.A compelling infographic would present the nutritional data in a digestible format, avoiding overwhelming the reader with dense text. The use of color-coding and strategic layout is crucial for this purpose.
Infographic Design and Elements
The infographic could be designed as a circular pie chart, with each segment representing a macronutrient: fat, protein, and carbohydrates. The largest segment, representing fat, would be a deep cream color, reflecting the cream’s high fat content. A smaller, light beige segment would represent protein, and a very small, almost negligible, light brown segment would show the minimal carbohydrate content.
Clear labels would specify the percentage contribution of each macronutrient to the total calorie count. The total calorie count per serving (e.g., per tablespoon) would be prominently displayed in a bold, easily readable font. A separate section could list key micronutrients, such as vitamin A and vitamin D, using small, easily understandable icons next to their values.
The background color of the infographic should be a light, neutral tone to avoid distracting from the data. A simple, clean font should be used throughout for optimal readability. The overall design should aim for a professional, yet approachable aesthetic, ensuring clarity and ease of comprehension.
Effective Communication of Nutritional Content, Nutrition facts in heavy whipping cream
This visual representation, with its clear color-coding, concise labels, and strategic layout, allows consumers to quickly grasp the nutritional composition of heavy whipping cream. The pie chart visually emphasizes the high fat content, enabling a quick comparison with other dairy products or healthier alternatives. The prominent display of the calorie count per serving provides consumers with crucial information for portion control and calorie management.
The inclusion of key micronutrients provides a more complete picture of the nutritional profile, moving beyond a simple macronutrient breakdown. The infographic’s design aims to transform complex nutritional data into a readily accessible and easily understood format, ultimately empowering consumers to make informed choices.
Questions and Answers
Is heavy whipping cream suitable for baking?
Yes, heavy whipping cream is ideal for baking as it adds richness and moisture to many recipes, particularly those requiring a creamy texture.
Can I substitute heavy whipping cream with something healthier?
Yes, consider alternatives like coconut cream, almond cream, or low-fat milk alternatives, though the taste and texture may differ.
How long can I store opened heavy whipping cream?
Store opened heavy whipping cream in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 5-7 days.
Does heavy whipping cream contain lactose?
Yes, heavy whipping cream contains lactose, making it unsuitable for individuals with lactose intolerance.
